میکسر پیوسته – کامسول
Continuous Mixer
اختلاط مداوم در تجهیزات فرآیند برای مخلوط کردن اجزا در یک پاس استفاده می شود. در مقایسه با اختلاط دسته ای، این عملیات دارای این مزیت است که مراحل پر کردن و تخلیه مخزن حذف می شود، به این معنی که فرآیند می تواند بدون وقفه اجرا شود. عیب اختلاط مداوم این است که زمانی که مواد در میکسر می گذرد، یعنی زمان ماند، ثابت نیست. زمان اقامت تا حد زیادی به جزئیات ساخت میکسر و عملکرد آن بستگی دارد. پارامترهایی که بر زمان اقامت تأثیر می گذارند، به عنوان مثال موقعیت و سرعت پروانه و نرخ تغذیه در ورودی است.
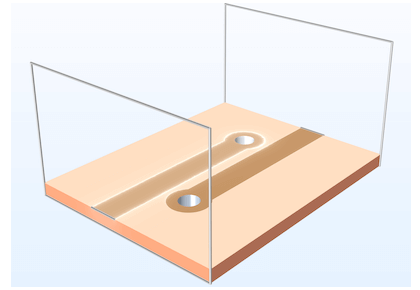
در این مدل یک مخزن با یک پروانه نامتقارن مدل سازی شده است. هندسه مخزن و پروانه با استفاده از قطعات کتابخانه قطعات ماژول Mixer تعریف شده است.
یک مایع به طور مداوم از طریق یک ورودی نزدیک بالا به مخزن تغذیه می شود. سپس مایع از طریق یک خروجی در پایین خارج می شود. میدان جریان آشفته ناشی از هم زدن پروانه برای استفاده از تحلیل روتور منجمد حل شده است.
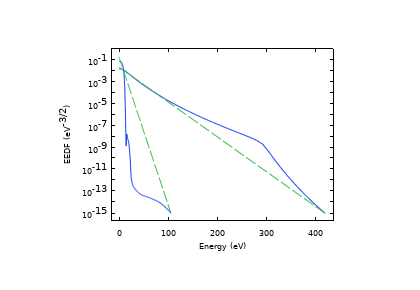
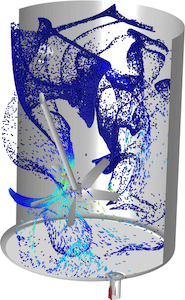
این مدل نحوه تجسم اختلاط و محاسبه توزیع زمان اقامت با استفاده از ردیابی ذرات را نشان میدهد. یک پالس حاوی 50000 ذره بدون جرم تزریق می شود و همانطور که از طریق میکسر جریان می یابد، ردیابی می شود. توزیع زمان اقامت با شمارش تعداد ذراتی که در یک زمان معین به خروجی رسیده اند محاسبه می شود.
Continuous mixing is used in process equipment to mix components in a single pass. Compared to batch mixing, this operation has the advantage that the tank filling and emptying steps are eliminated, implying that the process can be run without interruptions. A disadvantage of continuous mixing is that the time that the material spends in the mixer, the residence time, is not constant. The residence time is to a large extent dependent on the details of the mixer construction and the operation. Parameters that affect the residence time are for example the position and speed of the impeller and the feed rate at the inlet.
In this model a tank with an asymmetrically positioned impeller is modeled. The tank and impeller geometry are defined using parts from the Mixer Module Parts Library.
A liquid is continuously fed to the tank through an inlet near the top. The liquid then exits through an outlet at the bottom. The turbulent flow field resulting from the impeller agitation is solved for using a frozen rotor analysis.
The model shows how to visualize the mixing, and compute the residence time distribution using particle tracing. A pulse containing 50000 massless particles is injected and tracked as it flows through the mixer. The residence time distribution is computed by counting the number of particles that have reached the outlet at a certain time.
- COMSOL Multiphysics® and
- Particle Tracing Module and
- either the CFD Module, or Heat Transfer Module and
- either the CFD Module, or Polymer Flow Module
- لینک دانلود به صورت پارت های 1 گیگابایتی در فایل های ZIP ارائه شده است.
- در صورتی که به هر دلیل موفق به دانلود فایل مورد نظر نشدید به ما اطلاع دهید.
برای مشاهده لینک دانلود لطفا وارد حساب کاربری خود شوید!
وارد شویدپسورد فایل : پسورد ندارد گزارش خرابی لینک